Virtual Private Network (VPN)
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. Virtual Private Networking is a method that allows users to connect to sites, services or other users over internet through a private, encrypted and a more secure medium, generally called as “tunnel”.
VPN was initially designed to provide remote access to a company’s propriety applications and resources to their remote employees. However, as the idea flourished, VPN is now used for privacy, anonymity and bypassing judiciary censorship over certain services on internet; for example, geo-restrictions and blockades as well.
It is 2020 and we spend two-third of our day lingering over internet. We access many sites, applications and services. And, most probably, leave valuable traces behind. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) over public network is one of the easiest ways to ensure privacy and security; a best way to keep your private information private and reduce the risks of data interception.
The Vulnerability
An Analogy
A simple analogy would be better to understand the concept. Let’s get funky and consider you are in a classroom. While you are sitting at the last bench, your girlfriend is sitting at the first row. You want to send a message. What you would do is- take a piece of paper, write down the message. You pass it to your friend and your friend passes it to your other friend until it reaches to your girlfriend. Now, not all of your friends are genuine. Some of them can be foxy enough to open your paper and read it. And, alas, everybody knows what you two were talking about. This is one of the vulnerabilities of Internet.
Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks. There are millions of routers that are sitting on internet. If one computer tries to send a piece of information to another computer over internet, first, the information is broken down in several data packets. Then those data packets travel through different routers before reaching to a designated receiver. During this process, the routers does not just route the information but the actual data packets pass through them. Thus, if there is a person dedicated enough, he can gain access to these data packets sent over internet. These data packets are not just casual emails or messages but can also contain sensitive information like your e-Banking Details, Social Security Number and so on that you register over several occasions under several wireless networks; also, their metadata can reveal your IP address, the origin of information and your location. Thus, they need to be protected. This is where VPN makes an entry.
The Working of a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a tunnel between end-to-end users that cannot be accessed by other unauthorized users. When you subscribe to a VPN service, the whole traffic from your device is routed through your chosen VPN server instead of your Internet Service Provider. While doing this, your IP address is masked by the VPN server’s IP address, thereby, making you anonymous. Moreover, a VPN tunnel authenticates and encrypts the data you send over internet using their central technology called VPN Protocol.
When you are not using a VPN, every activity can be traced back to you easily. IP-address is a household name in Internet. Every device is assigned a unique IP address; your phone, your laptop, your router has their own IP addresses. When these devices access certain sites or services, they leave their IP address behind. Most web servers log your IP address into their system for various purposes. This IP address can be deduced down to your physical location, making you geographically trackable. So, let’s say, if you do some suspicious activity on Internet then you are vulnerable to get caught or tracked by your ISP, government or an “enemy”. Your whole internet browsing activity and history can be accessed through ISP. The hornet’s nest is not just your location but the information you share over internet. For example, you are on a local shop and complete your payment via a local Wi-Fi Network; you never know who is behind the Wi-Fi connection as it is not always from a trusted source and since it is open, anyone on the same network can intercept and catch your data packets. Every message, photos, e-mails, passwords you made via that open network can be caught, even your banking details.

However, if you are using a VPN service then you are safe. First, the VPN tunnel is encrypted in itself so it is pretty hard to penetrate. Even if someone finds a way to intercept into the VPN tunnel, your data packets inside the tunnel are encrypted through their VPN protocol. So, when somebody catches the information you shared inside VPN tunnel, they cannot read it because VPN encryption scrambles all the data and is gibberish to read. Therefore, unless it reaches an exit node, it is practically impossible to decipher. But, what about your IP address? Well, as said earlier, when you are connected to a VPN service, you are actually accessing the internet through your VPN server. Thus, your IP address is now masked by your VPN server’s IP address. So, every search you make, each site you enter is logged through VPN server’s IP address. Consequently, making origin point of the information untraceable.
When you are subscribed to a VPN service, you can actually choose a number of remote VPN servers that can be located in any part of the world. Doing so, you will camouflage your real-time address, whilst, enabling yourself to detour around some government or political censorship.
VPN Client and VPN Gateway
For the operation of a VPN service, there are two basic requirements: a VPN gateway and a VPN client.
A VPN gateway is a type of networking device that connects two or more devices or networks together in a VPN infrastructure. In context of VPN framework, a VPN gateway is responsible for enabling access to the end point of a VPN tunnel.
A VPN client is an end device, software or user that is seeking connection, network or data services from a VPN. Logging into a VPN client establishes a secure connection between the user and a VPN server.Nord VPN, Express VPN, TunnelBear VPN, etc. are some example of VPN client software.
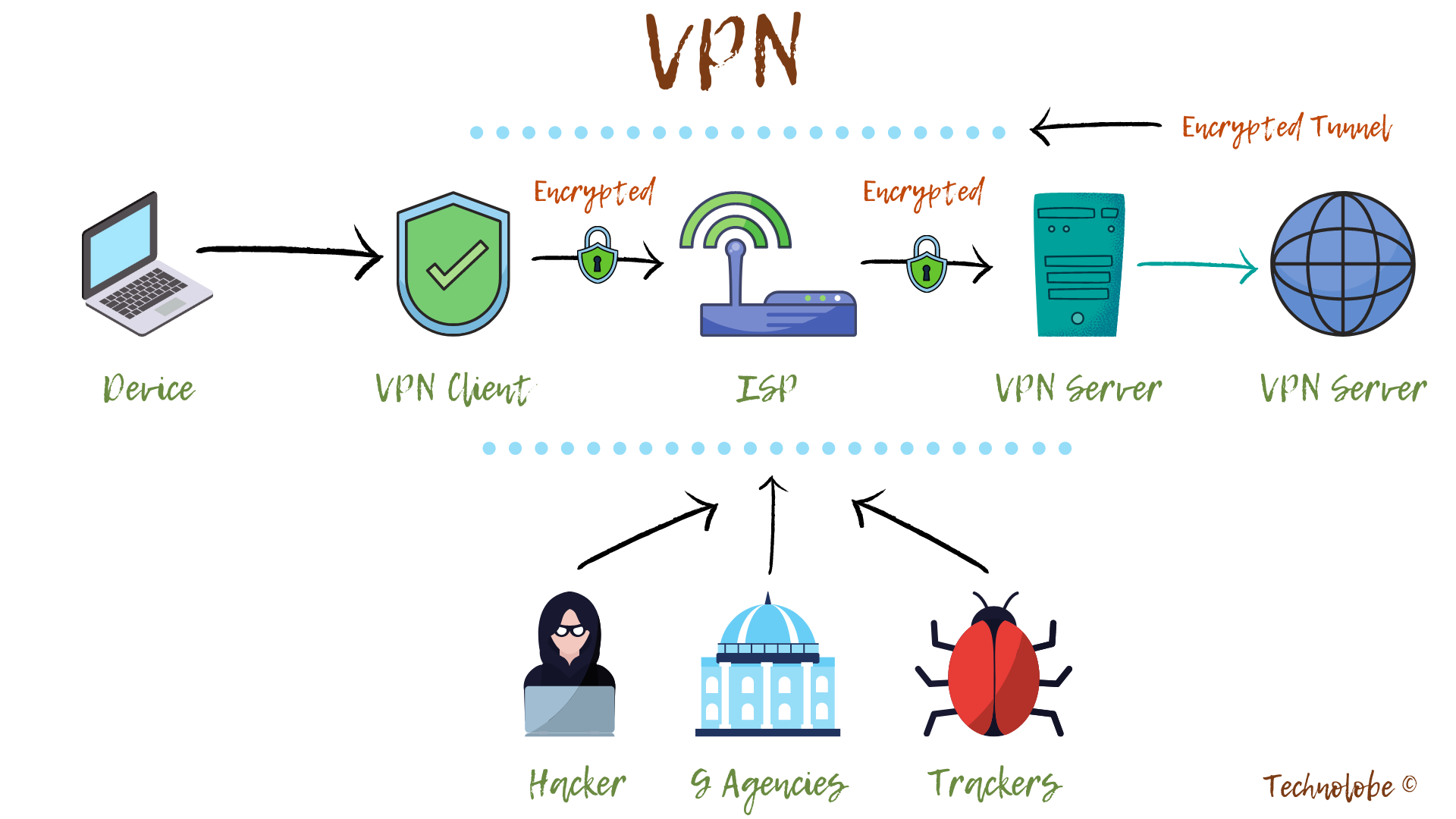
The VPN server needs to authenticate a VPN client before letting it communicate inside its VPN network. This is done by mutual sharing of data packets, usually, through a log-in process.
○ After the authentication is verified, the VPN software starts encrypting your data before sending it over to the VPN server ○ Once the VPN server receives all the encrypted information, it proceeds to decrypt it and forward it to designated web server ○ Correspondingly, when the VPN server receives the internet data you requested for (website login, for example), it encrypts it, and sends it back to the VPN client on your device ○ The VPN client then decrypts the information for you.
Encryption
The process of scrambling data or readable information into a code in such a way that it cannot be read without a very strong password, known as a key, is called encryption. In technical terms, it is the process of converting plaintext to ciphertext. It is done to prevent any unauthorized access.
Encryption requires the use of an encryption key: a set of mathematical values that both the sender and the recipient of an encrypted message know. In a Virtual Private Network, encryption key is accessible only to the VPN client and server.
VPN Protocol
A protocol is a standard set of rules that allow electronic devices to communicate with each other. A VPN protocol is a technology – based on a series of rules and logic – used by a VPN server for an effective transmission of your data and safety of traffic. Some of the commonly used VPN Protocols are listed below: –
- Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP/IPsec)
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
- Internet Key Exchange, version 2 (IKEv2)
- OpenVPN
Benefits of using a Virtual Private Network
The basic advantages one acquires upon using a virtual private network is summed below: –
-
Improved Privacy & Security
VPN enhances privacy by simply making you anonymous on Internet. Many applications and websites track your information, log and analyze your data, also, sell them for profit. Having said that, VPN can mask your IP address, location and web activity, thereby, making websites, web application and ISPs unable to identify the origin of your data. VPN also improves your web security by creating an encrypted path for data transition; hence, diminishing its vulnerability to intruders. Long story short, VPN encrypts your data traffic in a network.

However, if you are logged into certain websites like Facebook, YouTube, Google or such, you are constantly been tracked. On the account of their terms and conditions, you are actually giving them permissions to track, log and send your data back to their private servers. This is why you get ads and recommendations based on your web interaction.
-
Secured Remote Access
Did you know VPN was first introduced by Microsoft with their Point to Point Transfer Protocol (PPTP)? Big companies enforced Virtual Private Networking to make the transfer of important data safe and secure between their users and domain. It also enabled employees to work from home since they could access the data, resources and confidential information that is only available inside company’s network.

VPN pioneered remote network access not just by enabling employees to ingress into their master network but by providing a safe path for data transfer. Therefore, preventing the confidential information and business data from getting compromised. A university’s e-library is another example of remote network access through VPN; now-a-days universities are adapting VPN to share their resources like books, articles and private research papers among their tie-ups outside the university premises. Similarly, people also use VPN to access files stored in their computer or NAS (Network Attached Storage) from any part of the world.
-
Bypass Firewalls, Region-blocked contents & Geo-Restriction
VPN can help you effectively bypass firewalls. A Firewall is a network security system based on a set of predetermined security rules that governs incoming and outgoing network traffic. Sometimes, network administrators in school, colleges, office, airport and hotel prevent you from accessing certain websites because of their ordinance. Fortunately, you can bypass a Firewall restriction just by connecting to a VPN server.

Similarly, being connected to a VPN server can help you access region-blocked contents from various streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, Amazon Prime and such by masking your IP address with that of a VPN server based on a different location; consequently, mimicking your coordinates to a different nation. On top of that, if your country has enforced some judicial censorship over certain websites, application or services, using a VPN can help you steer them clear.
Please check your country’s legality regarding the usage of VPN. Most countries allow using VPN without any hassle. However, countries like China, Iran, Belarus, UAE, Oman, Iraq and Russia have some strong formulated laws regarding VPNs and its service.
-
Safe Torrenting & Ad-blocking
These days most VPNs come with an in-built ad-blocker and offer an elemental protection from malwares and trackers. Often, websites have ads and disturbing pop-ups everywhere along with some nefarious trackers and malwares that trace your entire browsing activity. VPNs usually offer a default ad-blocking, thereby, making your web experience clean and annoyance free.

One of the forfeits of P2P sharing or torrenting is the IP leak. Torrenting involves simultaneous downloading and seeding of data. During this time, the IP address of seeds and peers is revealed amongst the active connections. At the same time, ISPs can throttle your network speed because torrenting can, sometime, consume high bandwidth. This is done to ensure that other devices in the same network aren’t affected because of your high bandwidth consumption. Nevertheless, VPN ensures your anonymity over internet, therefore, liberating you of these obstacles.
Parting Words
I hope you can now extrapolate the gravity of Virtual Private Networking in your daily/work internet life.
While we talked about VPN and its importance, the problem may still persist about which VPN to choose for. And are VPN trustworthy? Well, even though VPNs are intended to protect users online, not all of them rightfully do so. There are many incidents where VPN companies (mostly free VPNs) have been found selling their user data to third parties. I would always suggest you to do your research and read the terms and conditions properly before signing up for a VPN subscription (I do not recommend free VPN if your prime concern is privacy). Also, choose a VPN application which offers services across all platforms. Take your time and decide wisely. Afterall, privacy is worth all time and money.
Tech enthusiast and a movie fanatic.








2 Replies to Understanding VPN: A Surficial Exploration
How To Remove Bloatware From Any Xiaomi Devices (Without Root): Easiest Way!
Fantastic Windows 10 Icons And How To Install Them
Best 24-Inch Monitors for Work From Home: June 2020!
The Minimalist Setup for Android Devices
Realme Watch 2 Launched: A Worthy Upgrade?
iQoo 7 Launched: Price, Specifications & Launch Date in India
Mi 11 Ultra: Into The Reckoning !!!
Surface Laptop Go Launched in India: The Most Affordable Surface!