This decade is probably the most revolutionary period for smartphones. We can see the long jump mobile phones have made from a clicking numpad to display running around bezels and back. The most important thing is smartphones are developing faster than PCs right now. So, here is our take on System on a Chip a.k.a SoC which made it all possible.
System on a Chip (SoC)
To begin with, SoC is a small chip that runs your phone. They house multiple processing units, modem, memory and other minute pieces together on small chip to save space and power. It is the brain of your smartphone. SoC is attached with wires and printed boards to communicate with other integral parts like camera, display, storage, etc.
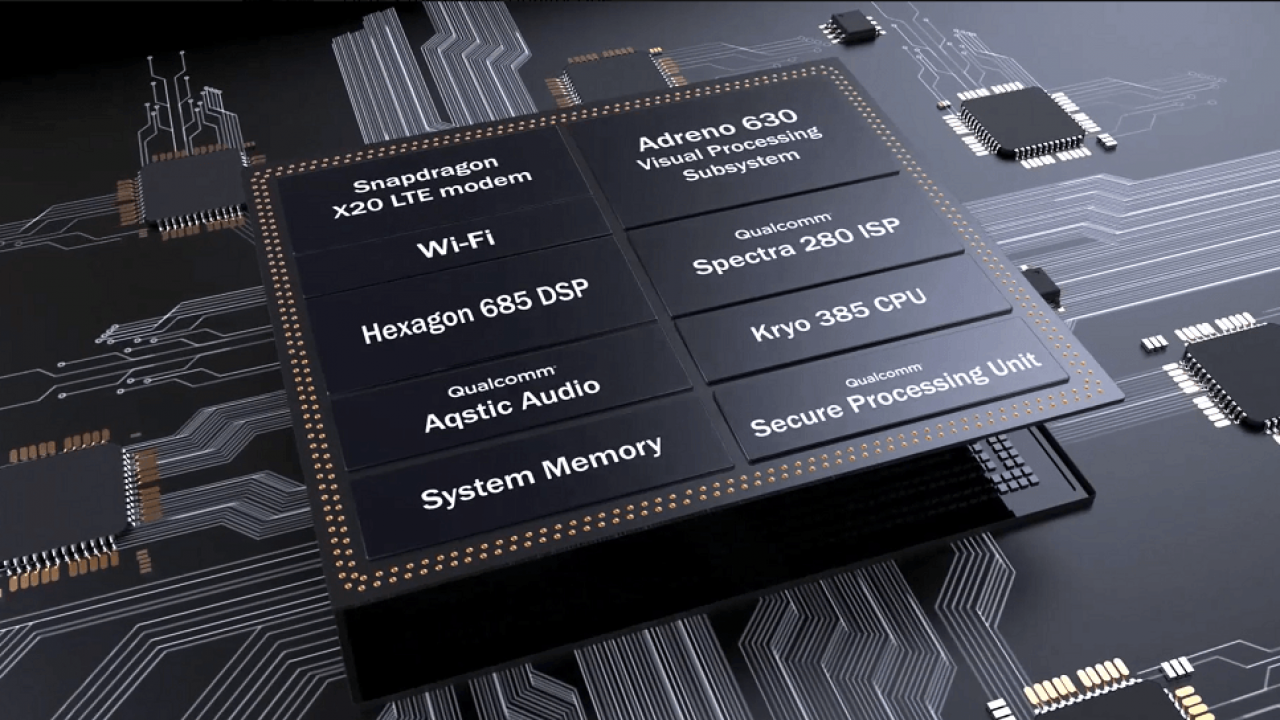
These are the basic components that a System on a Chip packs.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- Image Signal Processing (ISP)
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
- Neural Processing Unit (NPU)
- Memory
- Northbridge
- Modems
| CPU | The “brain” of the SoC. Responsible for processing all the data into codes. Running your software and apps |
| GPU | Runs/Renders the 2d/3d animations, your beautiful games. Also has a crucial role in multimedia support |
| ISP | Converts data from your camera into image and video files. |
| DSP | They are used where ever you require real-time processing of your real-time inputs. Image processing, Audio processing, Signal conditioning. For example, features like gestures, face detection, anti-shake. |
| NPU | Handles the machine learning tasks of your smartphone. Normally AI like voice recognition, camera processing. |
| Modems | Coverts the wireless signals (cellular radios, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi) into data your phone understands. |
| Northbridge | Acts as an interface between CPU and rest of your chipset. |
Some household names of chipset manufacturers are QUALCOMM, MediaTek, Samsung’s Semiconductor, Huawei’s HiSilicon and NVidia Tegra.
Processor
The most determining factor for the performance of a smartphone is its processor. The popular are amongst Qualcomm’s Snapdragon, MediaTek’s Helios, Samsung’s Exynos and Apple’s Bionic Chip. These chips are available in wide range varying according to the budget and flagship-ness of a device.
What most people confuse about is the way they are named. Like, weird it is right? No, it isn’t. Just a little bit of words and you are clear as a sky after rain. The funda of naming is- as the number increases in the series, the performance and efficiency increases.
For example: Snapdragon 730G is better than snapdragon 626. Snapdragon 865 is better than all snapdragons at the moment. A12 bionic chip > A11 bionic chip.
Qualcomm Snapdragon
This US based company for semiconductor technology is one of the largest manufacturers of smartphone processor. They name their processors under Snapdragon brand (Like Xiaomi releasing phones under Redmi and MI sub-brands).
The Snapdragon processors are released under various series, below is the simplest explanation:
Snapdragon 200 and 400 series – They are the least performing and cheapest of all. They are found in the least expensive phones in market. Qualcomm 205, Snapdragon 450, Snapdragon 435, Snapdragon 430 are some examples.
Snapdragon 600 and 700 series – These series of chips are found in the budget friendly smartphones. The 600 series is typically in the lower budget ($200~$300) while 700 series on the mid-tier smartphones ($300-$500). Snapdragon 625, Snapdragon 626, Snapdragon 650, Snapdragon 720, Snapdragon 730/730G are some examples of this series.
Snapdragon 800 series – These series of processors are found in flagships of devices which are typically to set a stature in device performance. They are found in high-end devices. For example, Snapdragon 865, Snapdragon 845.
Now, if we go on explaining the processors of each brand it is going to get boring and long. So, here it is in brief. Apple’s Bionic A chip (A8, A9, A10, A13). MediaTek Helio X (for budget phones) and P (for high-end devices). MediaTek Helio P60, P70, Helio X20, X30 are few examples. HiSilicon releases Kirin processors for its owner company Huawei. While Samsung releases Exynos processors for their phones outside USA.
Besides this basic naming, here are the factors that determines the flagship of a processor.
Architecture
The architecture of CPU determines how efficient it is. They are like the floor plans of the building, more organized they are- is easier and efficient for you to live in. ARM is the industry leading company that designs the core for most Smartphone processors.
Today’s smartphones have ARMv8-A architecture for mobile processing. The ARMv8 A series label their processors as ARM Cortex A-7X (Cortex A-77, Cortex A-76, Cortex A-75) for leadership performance, ARM Cortex A-6X and A-5X (Cortex A- 65, Cortex A-55, Cortex A-53) for balanced performance and efficiency while ARM A-3X for least efficient ones.
While ARM licenses their CPU core designs. Hardware manufacturers like Qualcomm, Apple, Samsung, NVidia hold architectural license and core license as well. The architectural license lets the company to use their processors. Whereas, the core license enables company to use their processors as well as being able to build their own cores.
For example, Qualcomm’s 1st gen processors use ARM Cortex-A whereas the 2nd gen uses both the Cortex-A and its own designed kyro cores. Likewise, Apple uses their own Swift core which was their first custom core used in iPhone 5 and Samsung’s custom core named Mongoose in their Exynos processors.

Clock Speed
Clock Speed is the rate at which a processor can process the given set of instructions. It is normally expressed in terms of Hertz (GHz or MHz). If the clock speed is higher, the processing becomes faster. The phone becomes more responsive towards the tasks like gaming and browsing.
For example, if a processor has 3GHz speed- it can process 3 Billion of information per second which is better than 2GHz.
The downside is higher the clock speed, more heat is dissipated and more battery is consumed.
Number of Cores
We have been hearing a lot of quad-core processors or octa-core in processors. Well, it means how many cores does a processor have. Having greater number of cores can distribute tasks, decrease heat dissipation and conserve energy.
Having cores at only certain clock speed can have both performance and power consumption issues. For example, if your CPU is clocked at 1.5GHz it can save energy but struggles in heavy tasks. Whereas having your CPU clocked at 2.8 GHz can assure you performance but it consumes more battery and produces more heat. Thus, to overcome this ARM introduced big.LITTLE Technology.
big.LITTLE Technology groups different processors into clusters. The “big” cluster has high processing ability while the “little” cluster has better efficiency. For example: The 8 cores are arranged in two clusters. One cluster has four large powerful cores at higher clock speed and the other cluster has four small cores at lower clock speed for more efficiency. And the tasks can be distributed among these clusters as per their requirements.
Nano-meter Technology (Nm)
In a very simple sense, most of the electric components are made up of transistors. A processor is made by embedding a large number of transistors. Since they are so minute, they are measured in terms of nanometer (nm). Snapdragon 845 uses 10nm technology, Snapdragon 865 uses 7nm technology while Kirin 990 and Apple Bionic A13 chip uses 7nm + technology.
The nanometer defines/measures the path for current flow. The lesser the distance, the voltage needed to make electricity go across its paths gets smaller too. Thus, consuming less power and producing less heat. This ultimately increases the efficiency and battery life of your device.
GPU
That was a long talk about smartphone processors. GPU as the name suggests processes the graphics of your smartphone. It is very task-oriented and operates huge number of tasks on a parallel second. Remember the time when you are playing game! Those beautiful 3d animations, they are all processed by GPU.
Major GPUs in this silicon era are Adreno GPU by Qualcomm and Mali GPU by ARM.
Connectivity
Today’s devices comes with greater number of connectivity – 5G. 4G, 3G, WIFI, Bluetooth and GPS. They all require hardware support to send or receive signals, which is effectively made possible by Modems. The latest Snapdragon 865 supports 5G which is supposedly the next big thing in Communication Technology.

Pfft, that was a real long theory, wasn’t it? Hope you got information on what you were looking for. Next time, while trying to buy smartphones be sure to use the information that you just read. Thank you.
Tech enthusiast and a movie fanatic.








4 Replies to Everything about Smartphone Processors or SoCs
How To Remove Bloatware From Any Xiaomi Devices (Without Root): Easiest Way!
Fantastic Windows 10 Icons And How To Install Them
11 Best Magisk Modules You Need to Try
The Minimalist Setup for Android Devices
Realme Watch 2 Launched: A Worthy Upgrade?
iQoo 7 Launched: Price, Specifications & Launch Date in India
Mi 11 Ultra: Into The Reckoning !!!
Surface Laptop Go Launched in India: The Most Affordable Surface!